Treat Enlarged Prostate Effectively

of Experience



Care & Support
An enlarged prostate (BPH) can be effectively treated.
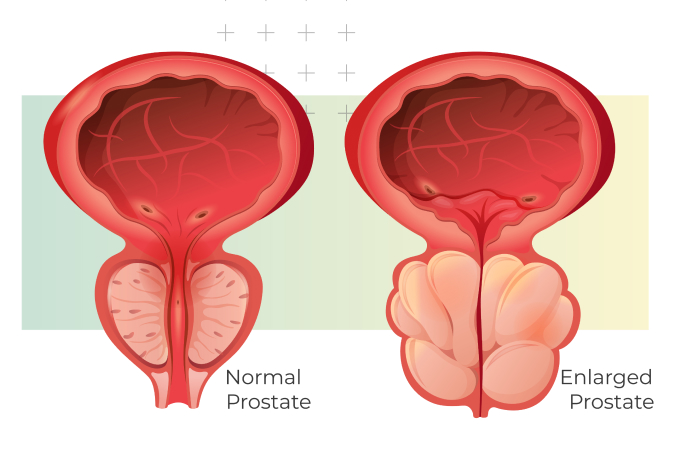
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Also known as an enlarged prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that often occurs in older men.
As the prostate enlarges, it can press against the urethra, leading to urinary issues such as frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, and a weak urine stream.
While BPH is not life-threatening, the symptoms can be bothersome and may require medical attention.
How Do I Know If I Have BPH?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) often causes urinary symptoms due to the enlarged prostate pressing on the urethra.
Common signs include:
Frequent Urination:
Needing to urinate more often, especially at night
Urgency:
A sudden, strong urge to urinate that can be hard to control
Weak Urine Stream:
Difficulty starting urination or a stream that is weaker than usual
Incomplete Emptying:
Feeling like the bladder doesn’t completely empty after urination
Urinary Dribbling:
A slow leak of urine even after you’ve finished urinating
Straining to Urinate:
Needing to push or strain to begin urination
How is BPH Diagnosed?
At TTW Urology, we take a comprehensive approach in diagnosing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) accurately. This may include:
Medical History
Our urologist will evaluate your symptoms, lifestyle, and any relevant medical history to assess the severity of your condition.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
This involves the urology doctor gently inserting a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to assess the size and shape of the prostate.
Urine Tests
These tests help rule out infections or other conditions that may be causing your symptoms.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
A blood test to measure PSA levels, which can indicate prostate enlargement or other prostate conditions.
Urine Flow Test
This test measures the strength and amount of urine flow, helping to determine how much BPH is affecting your bladder and urinary tract.
Bladder Scan
Imaging tests may be used to check how much urine remains in your bladder after urination and to measure the size of the prostate.
Urodynamic Testing
In some cases, tests to measure bladder pressure may be recommended to evaluate how well the bladder and urethra are functioning.
BPH can be treated via medications, minimally invasive procedures and surgery.
At TTW Urology, we tailor prostate enlargement treatment to each individual for optimal outcomes.
How is BPH Treated?
We offer a range of effective treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), tailored to your symptoms and overall health.
Treatment options include:

Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes like reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, practising bladder training, and managing fluid consumption can alleviate mild symptoms.

Medications
We may prescribe medications that relax the muscles in the prostate or shrink the gland to improve urine flow and reduce symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For moderate to severe cases, procedures like the UroLift or water vapour therapy can relieve obstruction with faster recovery times and minimal discomfort.
Surgical Treatment
In more advanced cases, surgery such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or prostatectomy may be necessary to remove the excess prostate tissue causing the blockage.
Need More Information?

Our BPH Specialist
Dr Tan Teck Wei
MBBS (S’pore), DFD (CAW), MRCS (Edin),MMed (Surgery), FAMS (Urology)
Dr Tan Teck Wei is a Senior Consultant Urologist who is skilled in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as an enlarged prostate; as well as treating complex urological cancers involving the kidneys, prostate, and bladder. Dr Tan is fellowship-trained in open, laparoscopic and robotic urologic surgery; and has held numerous leadership and academic positions. He understands the concerns faced by his patients and strives to provide effective and supportive care.
FAQs on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
No, BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate. Although some symptoms may be similar, BPH does not increase your risk of developing prostate cancer.
BPH typically occurs in men over the age of 50, with symptoms becoming more common as men age.
BPH does not usually resolve without treatment. However, mild symptoms may be managed with lifestyle changes, while more severe symptoms may require medication or other treatments.
If you experience bothersome symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent night-time urination, or a weak stream, seek BPH treatment to prevent complications like urinary retention or bladder infections.
Not everyone with BPH requires surgery. Mild to moderate symptoms are often treated with medications or minimally invasive procedures, while surgery may be recommended for more severe cases. Your doctor will determine the best treatment for your condition.
For enquiries on your condition or appointment booking, please fill in the enquiry form and we will be in touch with you soon. Your health and well-being are our top priorities, and we look forward to assisting you on your medical journey.



